How does inactivity from confinement affect my body?
What do I lose when I stop training? How long does it take to lose my physical shape? How long does it take to recover my physical condition?

In these difficult times for all triathletes we are already turning our heads and thinking how and when we can return to training with "normality".
This break has come without warning and from one day to the next all our routines and training plans have changed.
Many of us have already begun to wonder What do I lose when I stop training?,How long does it take to lose fitness?
And above all How long does it take to regain fitness? Well, all these doubts and some more we will resolve below.
First of all we must clarify that for a few days of inactivity nothing happens and they can even be beneficial to rest.
Thus, during the first days of inactivity, our body hardly undergoes changes and the physiological adaptations achieved through physical exercise are maintained almost entirely.
Once the date of the first 10 days it is when there begin to be changes in our organism affecting different aspects, which we will name below.
Vascular activity and pulsations
In this way, when we remain inactive for several days, we begin to lose the physiological adaptations achieved through regular exercise, and one of the first affected will be our heart.
This organ will decrease your ability to pump the same volume of blood to the body, so to provide the same supply you will have to beat faster.
Therefore, when returning to daily activity, it is normal to notice that our pulsations are slightly elevated when performing the same exercise compared to the pre-inactivity period.
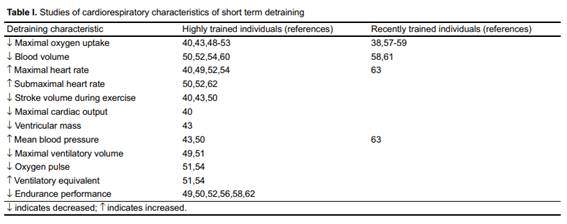
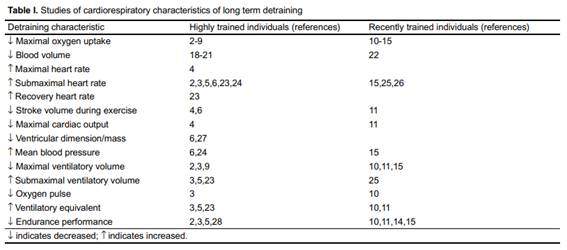
Lactic acid and glycogen stores
Another adaptation that is relatively easy to do is that of glycogen stores. These deposits store glucose and then provide us with energy when doing physical exercise.
As the days go by while idle the capacity of these glycogen stores is altered and it decreases with relative ease.
In addition, will decrease our body's ability to assimilate and recycle lactic acid. This decrease will directly affect our fitness state, anticipating the appearance of fatigue and muscle weakness.
VO2 Max
As for the maximum oxygen consumption (maximum amount of oxygen that the body can absorb, transport and consume in a given time), the first week will not show any significant change and will even be maintained.
But it has been shown that from the 10 days of inactivity en trained subjects can drop between 4% and 14% depending on the physical state of the athlete and the days of inactivity.
In addition, it will also decrease the ability of the muscle to use oxygen by altering the density of the capillaries, the amount of mitochondria and the oxidative enzymatic activity.
Basal Metabolism
Basal metabolism (the amount of energy the body needs in a state of complete rest and at a constant room temperature to maintain vital functions) will also be affected.
As our oxygen consumption drops, the amount of energy required to maintain vital functions will also decrease. Thus, our body will need less calories to function.
Muscles
Finally, the muscles will not be compromised especially during the first 10 days. As of the second week, as mentioned above, a decreased oxidative capacity of muscle, as well as a loss of muscle mass.
Experts assure that from the tenth day each day of inactivity we lose 0,5% of muscle mass.
Furthermore, this directly affects the ability of the muscle to generate strength and power, so these two aspects are affected.
It should be noted that the loss of muscle mass is also related to the subject's state and age.
What is the solution?
Well, once we know all this, the solution is easy ?.
We have to continue exercising as much as possible so that we do not lose in a month those physiological adaptations that we have achieved during so many months of effort and training.
Therefore, I recommend you make physical activity at least 3 times a week with a medium-high intensity, which includes both aerobic exercises for the cardiovascular system and for muscle strengthening.
Remember that if during this confinement you present any musculoskeletal ailment for staying in the same positions for a long time or during any exercise fisify (https://www.fisify.com/) is at your disposal to make any consultation with professional physiotherapists and solve the case by therapeutic exercise completely free of charge.
Bibliography
-
Mujika, I. & Padilla, S. (2000a). Detraining: loss of a training-induced physiological and performance adaptations. Part I. Sports Medicine, 30. 79-87.
-
Mujika, I. & Padilla, S (2000b). Detraining: loss of training-induced physiological and performance adaptations. Part II. Sports Medicine, 30. 145-154.
-
Bosquet, L. & Mujika, I. (2012). Detraining. Enduranve training - science and practice (pp. 99-106). Vitoria-Gasteiz, Basque Country -
Brooks, N., Cloutier, G., Cadena, S., Layne, J., Nelsen, C., Freed, A., Roubenoff, R., Castaneda-Sceppa, C., 2008. Resistance training and timed essential amino acidsprotect against the loss of muscle mass and strength during 28 days of bed restand energy deficit. J. Appl. Physiol. 105, 241–248.
-
De Boer, M., Selby, A., Atherton, P., Smith, K., Seynnes, O., Maganaris, C., Maffulli, N., Movin, T., Narici, M., Rennie, M. , 2007b. The temporal responses of proteinsynthesis, gene expression and cell signaling in human quadriceps muscle andpatellar tendon to disuse. J. Psychol. 585, 241–251.
There are no previous results.