Muscle tear? Fisiocos: Treatment with radio frequency / diathermic method
Surely many of you have asked yourself Why does a muscle break occur? A muscle injury can be caused by an external mechanism "contusion" or internal mechanism "by stretching". These injuries are produced by the application of a tensional force superior to the resistance of the tissue, when it is in eccentric contraction. A viscoelastic modification of the tissue is provoked.
What factors influence? Fatigue and tissue temperature are factors that can influence the mechanism of injury.
Depending on the degree of injury will affect more or less muscle tissue, occurring from a functional alteration to a break or total disinsertion with appearance of hematoma.
What are the phases? :
- Phase 1
o Bleeding
o Waste substances
o Inflammation
o Ischemic death
- Phase 2
o Waste cleaning
o Initiation of healing
o Circulatory restoration
- Phase 3
o Scarring
o Remodeling
o Integration
How does the Radio Frequency Diathermal Method help in muscle breaks?
Through this method we introduce temperature inside the fabric without feeling heat as the thermal increase occurs from the inside out.
With the increase of internal tissue temperature we are going to:
- Increase blood flow to the tissues in depth
- Promote the expulsion of catabolic wastes
- Increase the supply of oxygen
- Increase the cell membrane potential
- Stimulate the immune system
Biological changes that generate an increase in blood circulation and increased cellular metabolism that will promote the resorption of the hematoma and tissue regeneration, while having an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect.
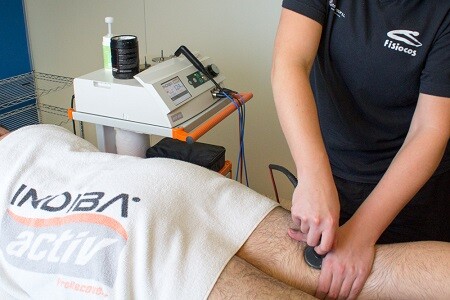
What is the treatment through INDIBA?
The muscle breaks should have a resting phase of about 3-5 days. From this phase, an active treatment combined with diathermy should be performed.
This increases the vascularization of the injured tissue, resorption of the hematoma, regeneration of the muscle fibers, fibrous scars are avoided, muscle functionality is recovered more quickly and the risk of recurrence is avoided.
Diathermy seems to be the physical therapy with which better results are achieved.
It can be applied from the third day of injury and follows this pattern:
From day 3 to day 7: Work to promote the resorption of the hematoma, circulatory restoration and help to form a stronger scar.
Diathermy on a daily basis combined with isometric muscle contractions. These isometric contractions should cause mild pain. They are performed during 6 "with 2 pauses" and for a few 5-10 minutes. Previously 20 minutes of treatment with diathermy with the muscle in position of relaxation is performed. (20 minutes diathermy with relaxed muscle / 5-10 minutes diathermy with muscle in isometric work).
From day 7 to 14: Work that allows a remodeling of the fibers in the direction of the tensile forces and a greater depth in the reorganization of the tissue.
Diathermy on a daily basis combined with isometric contractions and passive stretching. First, 15 minute of application with relaxed muscle, then 5 minutes performing isometric contractions of 6 "with 2 pauses". At the end passive stretching is performed to the point of bearable discomfort, it will be maintained during 12 "with 12 pauses" and for about 10 minutes, (15 minutes diathermy with relaxed muscle / 5 minutes diathermy with muscle in isometric work / 10 minutes diathermy with muscle in passive stretching work).
Depending on the degree of injury and evolution between the 14 day and 21 we work in search of getting a great depth in the remodeling of the fabric, a correct direction in the formation of the new fibers. If this is combined with neuromuscular stabilization work, controlled eccentric work and a correct return to training, the integration of the muscle in the movement pattern is favored and the possibility of recurrence is reduced in a high percentage.
For this, diathermy sessions are carried out every three days combined with passive stretching in three positions and active tension. For this work you have to review the state of the injury and decide times, positions and tensions in which you can work.
In summary: The most desired for the prognosis is a muscle regeneration as orderly as possible.
Large bruises, the destruction and disorganization of muscle tissue end up producing scars rich in disorganized fibrous tissue and this lack of contractile capacity. With what will be an area with a high probability of repetitive injury.
In addition, if the hematoma takes a long time to disappear, a muscle cyst may appear that will modify the work of the muscle and may cause pressure pain, being the technology applied by INDIBA a key aid in the resolution of muscle tears that helps and improves times and results for a quick recovery in case of muscle tears.
If you want more information about this therapy you can go to http://www.fisiocos.com/es
Author: Ferran Espejo
Director Advanced Unit Sports Recovery
Osteopath
FNR method
Hypopressive Method
Regenerative therapies
Visceral neuromyostatics
National Trainer Athletics
High performance specialist physiotherapist
There are no previous results.