The great forgotten of the body of the triathlete, the foot.
This article is in a certain way because of the great importance that they have, a vindication to the little case and to the little attention that we give to our feet.
Our collaborator Marian Sánchez tells us in this article what are the best exercises to take care of our feet.
If we think about it for a moment, the foot is the first part of our body that lands on the ground when running, which initially supports and absorbs all the load generated by the body and then distributes it throughout the lower limb and pelvis. Therefore, having a foot with a weak musculature, with lack of mobility, little cushioning or with any type of biomechanical pathology not solved, we can already imagine that it is going to be an important weak point in our body and that will lead us to two things : to perform less and have many more chances of injury, and not only on the foot, but it is sufficiently demonstrated that the reduction of mobility in the ankle joint increases the risk of injury to the Achilles tendon, knee (patellar tendinopathy) or of the goose foot, patellofemoral syndrome, fascia lata pathology, ACL rupture ...), and in the hip and pelvis.
As we often find ourselves in medicine, when an injury or pain appears in an area, the origin or the trigger is usually in another part of the body, and in lower limb injuries it is worth paying close attention to the feet ... and take care of them when there are no injuries, of course.
And by "taking care of them" I do not mean to take care of the nails and eliminate the basic hardness, but also that it is also essential to do a toning, strengthening and mobility of the muscles and joints of the foot.
Every time we have more assumed that to improve in triathlon it is important the work of general and specific strength and gym hours to perform better and injure ourselves less, when until recently this was unthinkable or we thought it was a loss of time to dedicate time to this when we could use it to do more meters in the pool, more hours of bike or run a few more kilometers of running a week.
That is to say, the concepts are changing and little by little it is giving more importance to other types of things, which make us perform more and better. I mean this with the work of the foot, it is not something that we have too integrated yet, but it is certainly something fundamental that will also make us be able to become better triathletes in the long term ... and avoid injuries, of course.
WHAT IS THE FOOT JOB?
FORCE AND PROPIOCEPTION
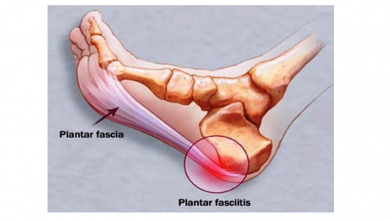
One of the basic points is to ensure that the muscles and joints of our feet are strong and efficient, as we do with the rest of the body's muscles. For this, it is essential that we stimulate the proprioception of our feet, and this is done by removing our shoes. One of the factors that make our feet vague and weaken the intrinsic muscles of the foot is the cushioning in footwear, and unfortunately (for the foot) this type of footwear is abused, both for running and daily use. The fact of placing a too thick layer of "material" between our feet and the floor makes that the muscles and joint structures of the feet have to work less because that cushioning work is already done by something external, oblivious to the foot, and with the passage of months and years, if you do not work in a specific way, the foot ends up becoming a really weak structure.
This specific work consists of "freeing ourselves" frequently when we can of the footwear to give life and stimuli to the feet, either getting used to being barefoot at home, to do a few minutes running barefoot after our training session if we have nearby grass or similar ... and when we have the opportunity, specific exercise routines like the ones shown below are also very effective, to stimulate more the intrinsic musculature, to separate and coordinate the fingers and free them from the "jail" that the footwear supposes for them:
FIRST FOOT FINGER
Yes, you have to pay special attention to the first toe. Why? Because it influences our biomechanics and injuries to the entire lower limb much more than we all think. A dysfunction of the first of the foot influences us every time we take a step, every time we jump and every time we run, since it is the toe that is responsible for taking off the foot on the ground. A hypomobility of the metatarsophalangeal joint of the first toe causes a compensatory movement and a change in the entire biomechanics of gait and running due to its relationship with the kinetic chain of the lower limbs, and can considerably increase the predisposition to injury, so it is something to keep in mind. And of course yes, when there are mobility limitations and / or deficits, you can also reeducate:
DEEP SQUAT OR SQUAT
Although the benefits of periodically and correctly performing the deep squat exercise are multiple and for the joints and tissues of all the lower limbs and spine, here we will focus more on its benefit to the foot, since it is a basic exercise for our ankles and feet. Having the ability to perform this gesture correctly will improve the range of mobility of the ankle, the flexibility of fascias of the foot and Achilles tendon, and improves the ability of the foot to better support the loads and at the same time to be more reactive in the takeoff of the foot of the ground. The deep squat, with or without weight, is always an interesting exercise to perform in our gym / strengthening session.
In addition, and although I have only talked about his work standing up and in relation to running, for a triathlete we can also imagine the importance of mobility and strength of the ankle and foot in swimming to be able to kick form correct and push efficiently to improve momentum in the pool. And the same happens in cycling, being able to make a functional and optimal dorsiflexion angle with the ankle during cycling pedaling is important to maintain the axis of forces of the lower limb and to exert our effort on the bicycle as efficiently as possible. . In addition, the point of support and all the forces in each push fall due to the position of the cleat on the heads of the metatarsals, so strengthening these structures and their muscles will make us have a stronger, more reactive point of support and have greater ability to perform an efficient and safe sporting gesture.
As we see, although in a generalized way there is little thought about its importance, the foot develops a fundamental point of reception and / or execution of forces in the biomechanics of the three triathlon disciplines, not only in running. Training and strengthening the muscles and joints of the feet through specific work will make us better athletes in general, and of course, it will help us in the long term to avoid injuries, an important point for which we also have to work in our training.
Mariam Sánchez
Further information: institutoinnova.net
There are no previous results.